

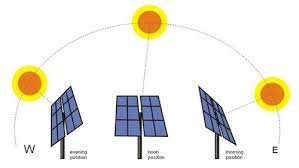
Solar tracker is a gadget that keeps a track of the movement of the sun and rotates itself according to the position of the sun. The solar trackers work by keeping the solar panels, or solar collectors pointed towards the sun directly. They change their position to absorb maximum tern amount of energy from the sun. With the help of the solar trackers, the output energy can be enhanced up to 30% more. Opting for solar trackers is a wise choice if you are looking forward to the amount of energy conserved from the increasing sun.

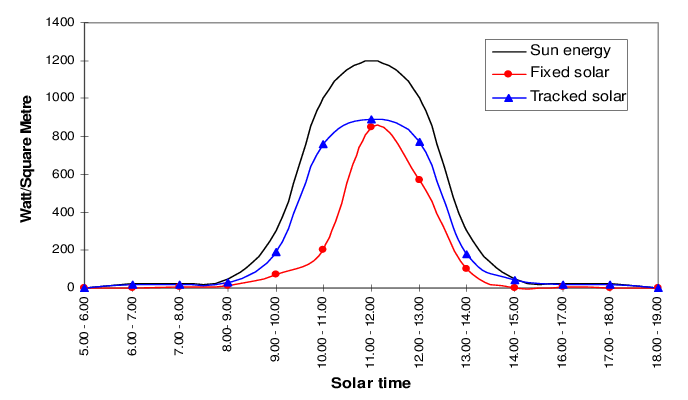
Competitive bidding creates a need for developers to examine technology solutions for superior generation to boost returns, in comparison to other solar developers. Solar tracker is the best way for conserving the maximum amount of solar energy by using a solar tracking system and by controlling the direction of the solar panels. Solar Trackers* are the ONLY known technology to boost energy generation for the same installed capacity of PV modules. Since 2010, 85% of UTILITY solar systems globally use trackers.

Self-powered system with smart performance communication architecture
ndependent balanced rows with +/-60° rotational range
Zero mechanical maintenance
Maximum GCR with the highest density of any tracker
Failure-free wind design
Flood clearance
Robotic cleaning ready, fast and simple installation


These kinds of trackers have four subdivision, they are
Horizontal single axis trackers (HSAT)
Vertical single axis trackers (VSAT)
Tilted single axis trackers (TSAT)
Polar aligned single axis trackers (PSAT)
Since these trackers only work on a single axis, they can move only in a single direction. These trackers are usually aligned on a North Meridian. Thought the direction of these trackers could be changed using the advanced algorithm.
Single-axis trackers will gather less energy per unit compared to dual-axis trackers, but with shorter racking heights, they require less space to install, creating a more concentrated system footprint and an easier model for operations and maintenance. Single-axis trackers are split into centralized and decentralized tracker types. Centralized or distributed trackers use a single motor to power a driveline between rows that will move an entire segment of panels. Decentralized systems have one motor per tracking row. There are also instances of trackers with motors present on every set of racking, making rows more adjustable during installation and in some cases allowing them to track independently of neighboring modules.

The Dual Axis trackers can two rotate in two degrees. It has two subdivision, they are:
Tip-tilt dual axis trackers (TTDAT)
Azimuth-altitude dual axis trackers (AADAT)
Since the Earth’s rotation relative to the sun is not the same all year, with an arc that will vary by season, a dual-axis tracking system will consistently experience greater energy yield than its single-axis counterpart since it can follow that path directly. A dual-axis solar tracker produces 30 to 45% more energy yield than fixed-tilt solar systems. Dual-axis trackers are used more in residential and smaller commercial applications but are beginning to see utility-scale deployment. Each of these trackers is installed atop a single elevated post to account for the greater range of angles the installed panels will reach. Dual-axis trackers can hold upwards of 20 panels per unit. With higher elevation, panels aren’t as easily accessible for cleaning. However, with more headspace, dual-axis trackers leave the ground underneath open for other purposes, such as agriculture or even carports.


Apart from changing direction, the solar trackers come with some additional benefits, they are:
They generate an extra amount of electricity in comparison with the fixed solar panels since they have extra exposure to the sun.
They come in binary formats that are the single axis and the dual axis. So, you can choose whichever suit your needs.
They need the same amount of space as fixed panels yet produce more electricity. So, they are a great option for land optimization.

Less than 400 pedestals per MW, lowest in its class
Least number of child parts
Up to 90 module ROWS
No welding or on-site fabrication required
Minimal install time